Orbital Blowout
Orbital blowout fractures result from increased intraocular pressure from a direct blow to the eye. By definition, these fractures have an inferiorly displaced orbital floor fracture without involvement of the orbital rim. Involvement of the lamina papyracea is commonly seen, since it also a weak wall of the orbit. Clinically, these fractures can present with enophthalmos and diplopia on upward gaze resulting from involvement of the inferior rectus muscle.
Scrollable Stack Images
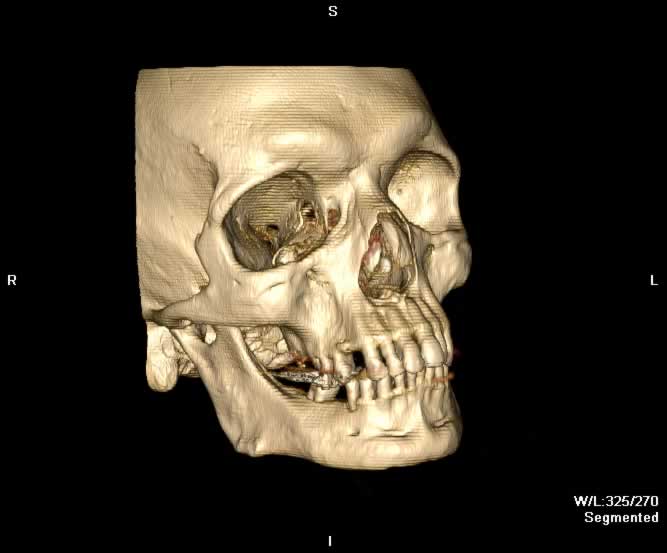
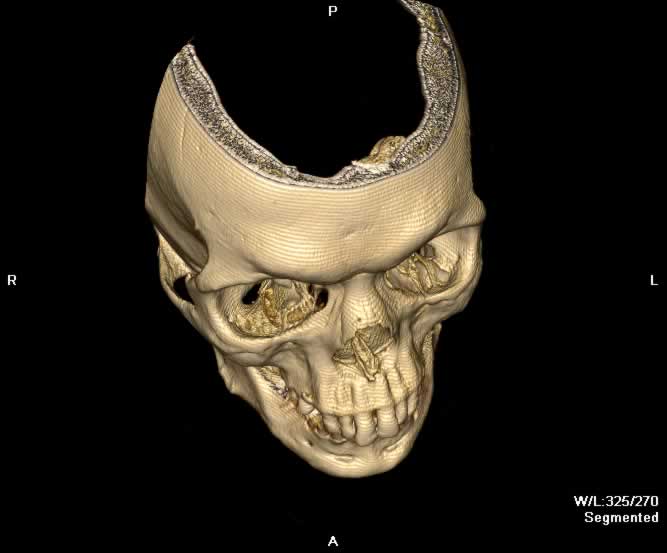
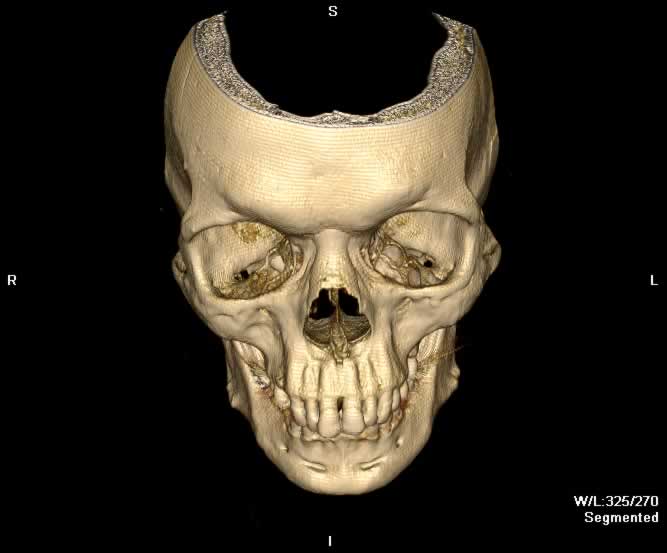
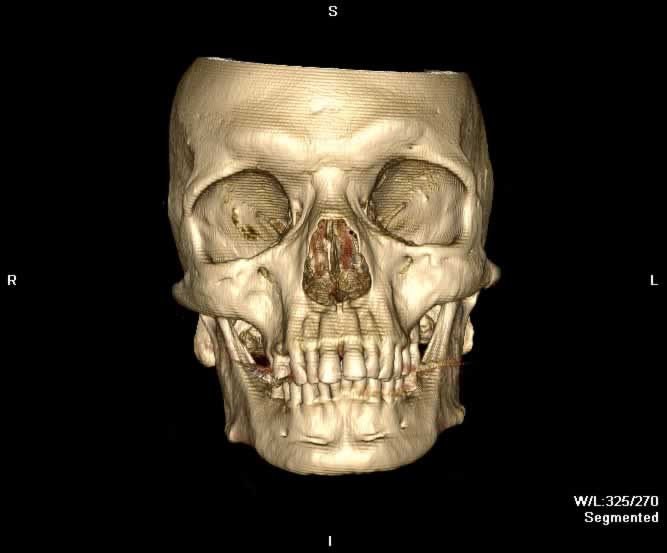
Images show a blowout fracture of the right medial and inferior orbital walls. Fracture fragments are displaced outward from the right orbit. Intraorbital fat herniates medially into the ethmoid sinus through a defect in the right lamina papyrecea and inferiorly into the maxillary sinus through a defect in the orbital floor. Inferior bowing of the right inferior rectus muscle into the orbital floor defect can be appreaciated. A depressed fracture of the anterior wall of the right maxillary sinus and hemorrhagic opacificaiton of the right maxillary sinus can be seen.
Static 2D
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Click to enlarge | |||
Static 3D
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Click to enlarge | |||
Rotating 3D

Return to top
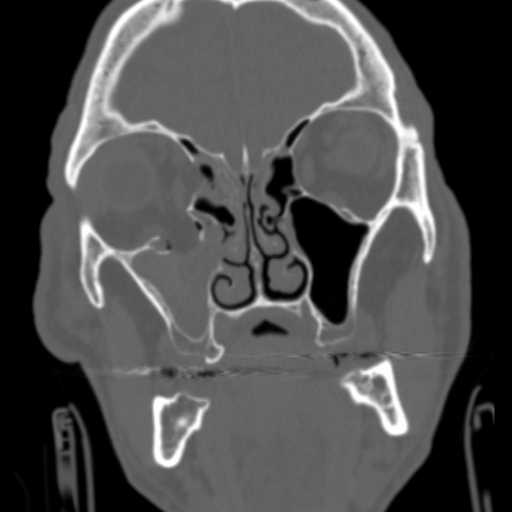
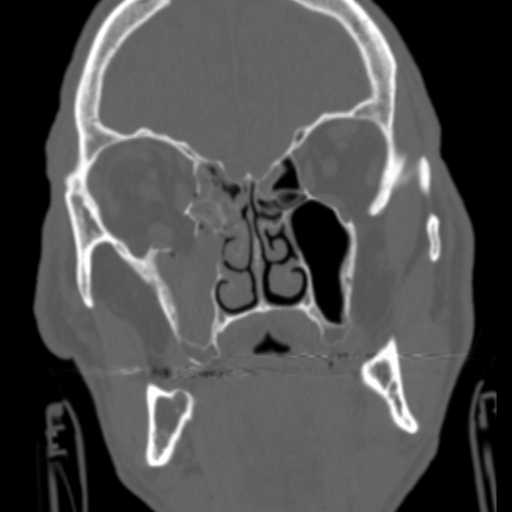
Coronal image demonstrates blowout fractures of the medial and inferior walls of the right orbit. Intraorbital fat herniates inferiorly into the right maxillary sinus, which demonstrates hemorrhagic opacificaiton.

Return to top
A more posterior coronal image demonstrates bony fragments of the medial and inferior walls of the right orbit outwardly displaced into the ethmoid and maxillary sinuses, respectively. The right inferior rectus muscle abuts an inferiorly displaced bony fragment of the orbital floor.

Return to top
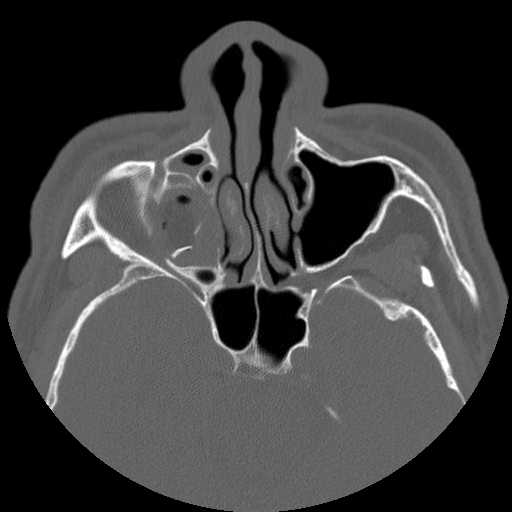
Axial image demonstrates fragmentation of the right lamina papyrecea and orbital floor with hemorrhagic opacification of the right maxillary sinus.

Return to top
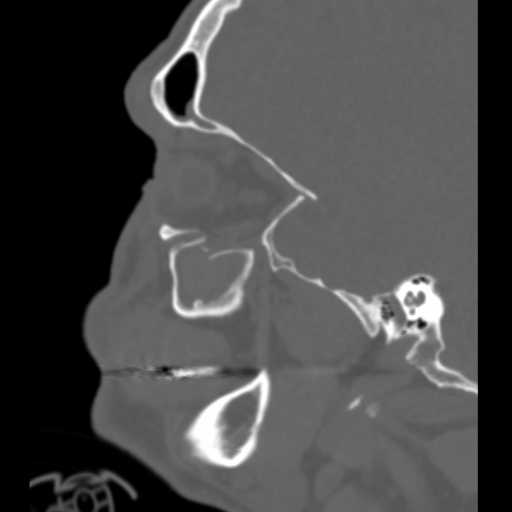
Sagittal image demonstrates slight bowing of the inferior rectus muscle inferiorly into a defect of the orbital floor. Bony fragments of the orbital floor are inferiorly displaced into the maxillary sinus.

Return to top

Return to top

Return to top

Return to top
Friends
 |
Orbital Rim |
 |
Frontal Sinus |
 |
Lamina Papyrecea |
 |
Orbital Floor |
Groups
 |
Orbital Fractures |
 |
Nasal Fractures |
 |
Tripod Fractures |
 |
LeFort Fractures |
 |
Smash Fractures |
 |
Mandibular Fractures |