
Lamina Papyrecea
The lamina papyracea is a paper thin portion of the ethmoid bone that constitutes the weakest portion of the medial orbital wall. Fractures of the lamina papyracea can be of the blow-in or blow-out variety. Both types can result in orbital emphysema and medial rectus entrapment resulting in diplopia. Blowout fractures result in herniation of intraorbital contents into the ethmoid sinus and occur frequently with orbital floor fractures.
Scrollable Stack Images
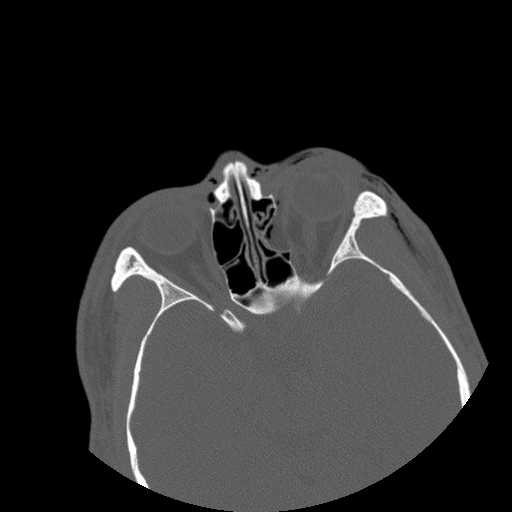
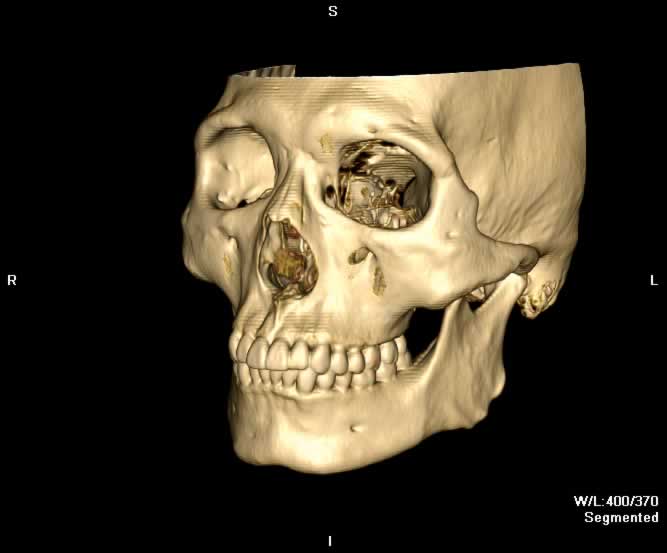
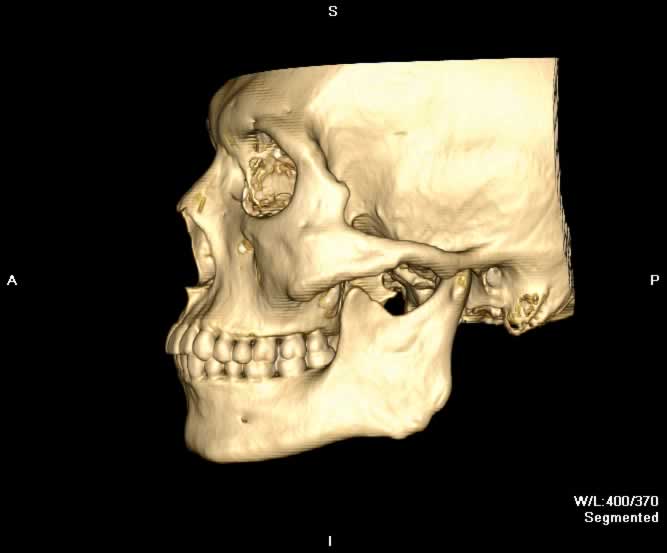
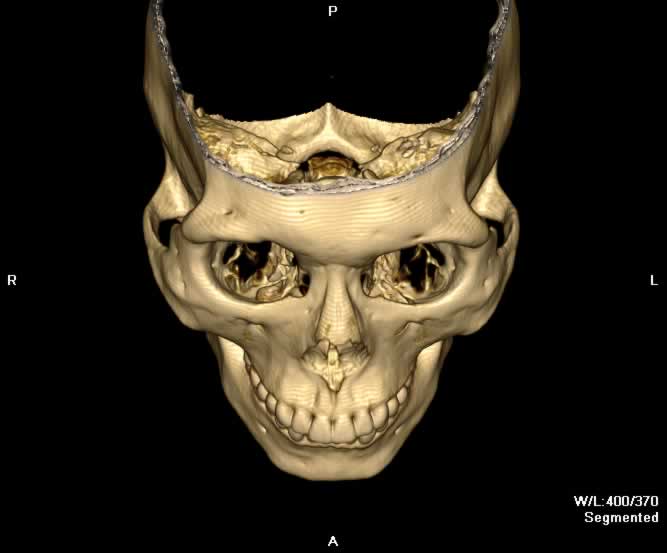
Images show a defect in the lamina papyrecea with herniation of intraorbital fat into the left ethmoid sinus. A portion of the left medial rectus muscle herniates into the defect, resulting in bowing of the muscle. Preseptal emphysema can be appreciated. The globe is intact and no other fractures are seen.
Static 2D
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Click to enlarge | |||
Static 3D
 |
 |
 |
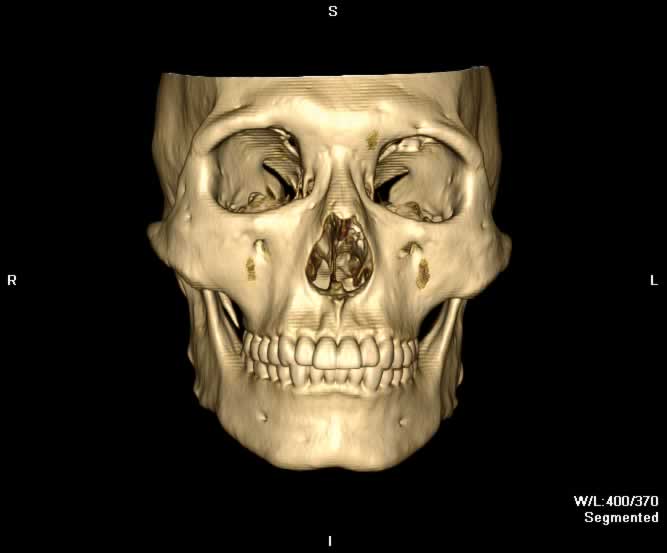 |
| Click to enlarge | |||
Rotating 3D

Return to top
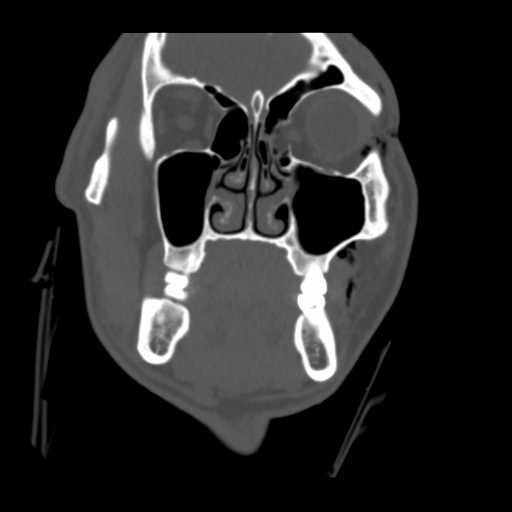
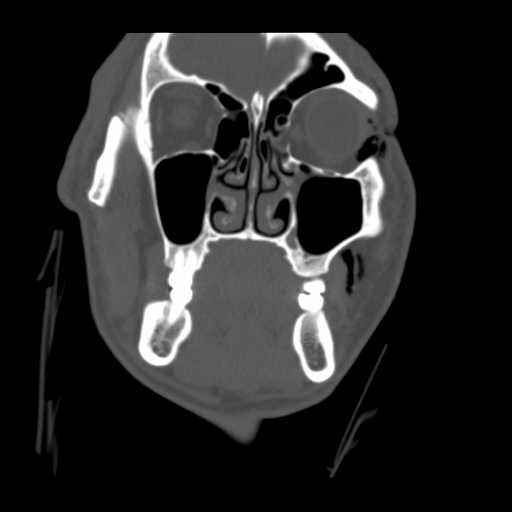
Coronal image demonstrates fat and a portion of the left medial rectus muscle herniating into the ethmoid sinus.

Return to top
A slightly more anterior coronal image demonstrates the bony defect in the left lamina papyrecea with herniation of intraorbital fat into the left ethmoid sinus.

Return to top
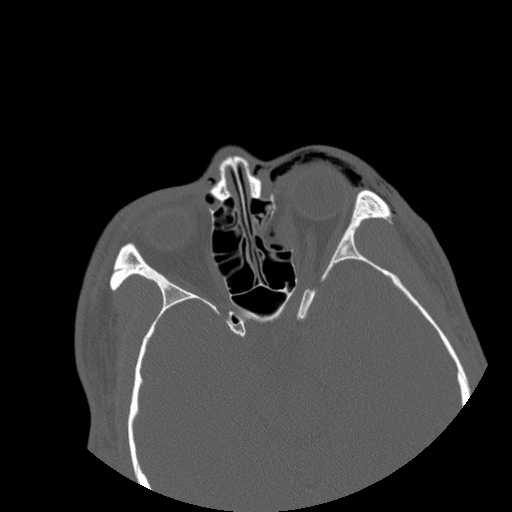
Axial image demonstrates displacement of the left lamina papyrecea into the ethmoid sinus. Extensive preseptal emphysema can be appreciated.

Return to top
Axial image demonstrates bowing of the left medial rectus muscle into the ethmoid sinus at the site of the bony defect.

Return to top

Return to top

Return to top

Return to top
Friends
 |
Orbital Rim |
 |
Frontal Sinus |
 |
Orbital Floor |
 |
Orbital Blowout |
Groups
 |
Orbital Fractures |
 |
Nasal Fractures |
 |
Tripod Fractures |
 |
LeFort Fractures |
 |
Smash Fractures |
 |
Mandibular Fractures |