
Frontal Sinus
Frontal sinus fractures include inner and outer table fractures and occur from direct forehead trauma or extension from nasoorbitoethmoid complex (NOE) fractures or severe orbital rim fractures. Fractures of the inner table rarely occur in isolation. Inner table fractures warrant surgical intervention as they can lead to meningitis and intracerebral abscess given open communication with the CSF space. The presence of orbital emphysema may suggest communication of frontal sinus fractures with the orbit.
Scrollable Stack Images
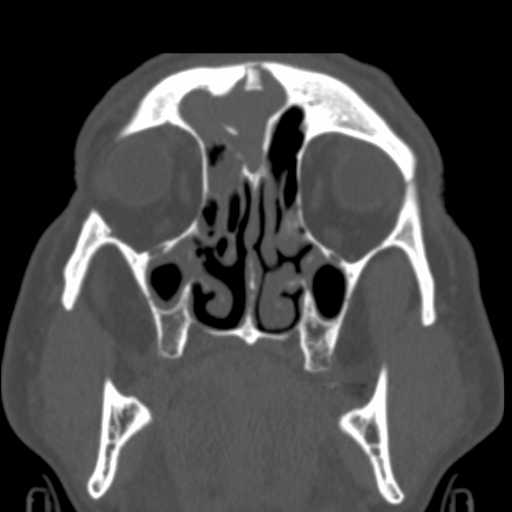
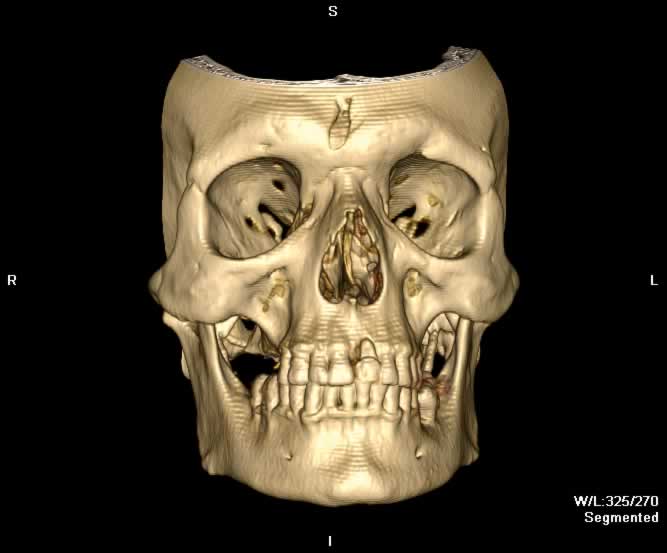
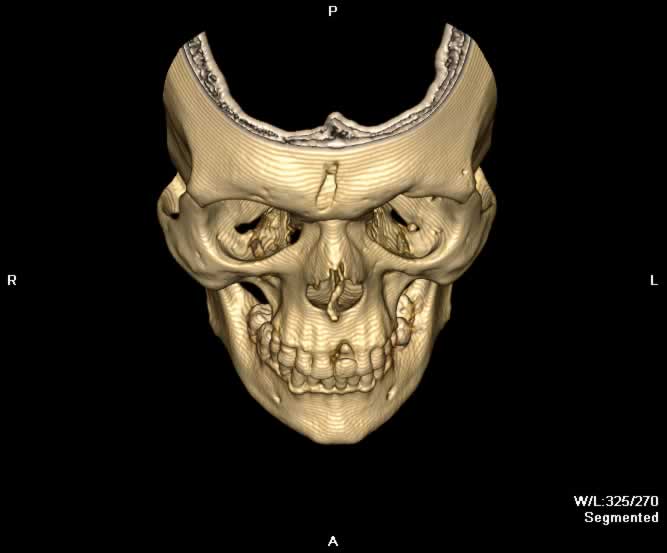
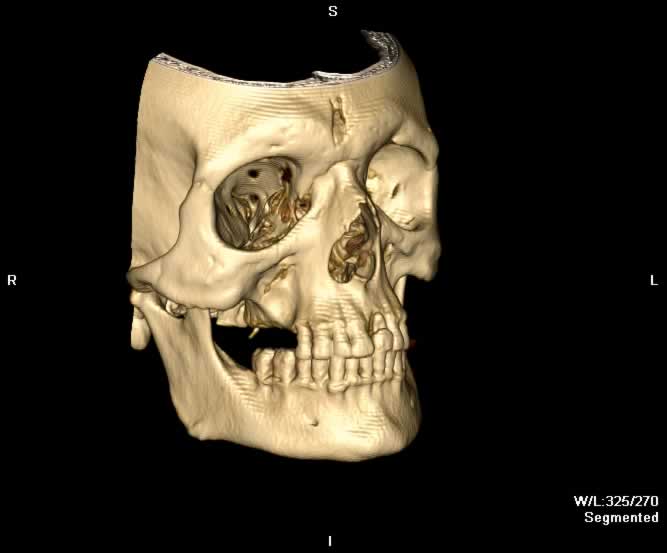
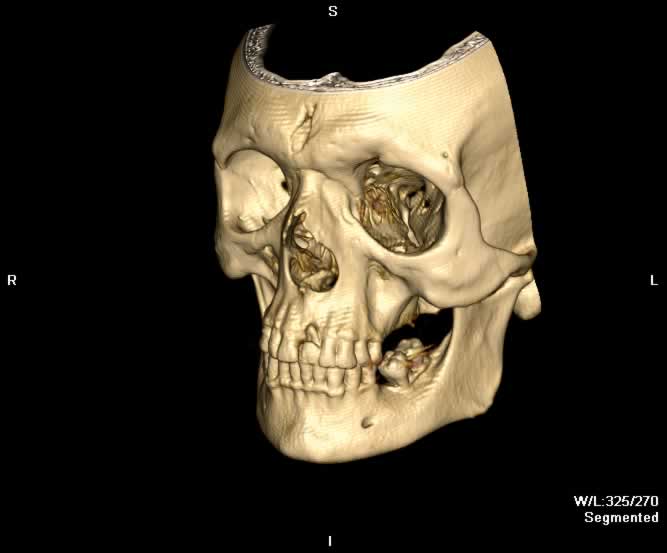
Images show a fragment of the outer table of the frontal bone posteriorly displaced in the midline. Fracture lines can be seen extending inferiorly through both the inner and outer tables of the frontal bone into the right nasal bone. Hemorrhagic opacification of the frontal and ethmoid sinuses is seen.
Static 2D
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Click to enlarge | |||
Static 3D
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Click to enlarge | |||
Rotating 3D

Return to top
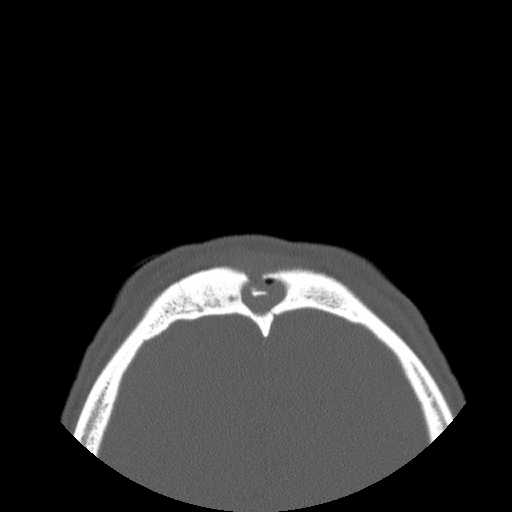
Axial image demonstrates a bony fragment of the outer table of the frontal bone posteriorly displaced into the frontal sinus. A fracture line through the inner table of the frontal bone can also be appreciated. There is hemorrhagic opacification of the frontal sinus.

Return to top
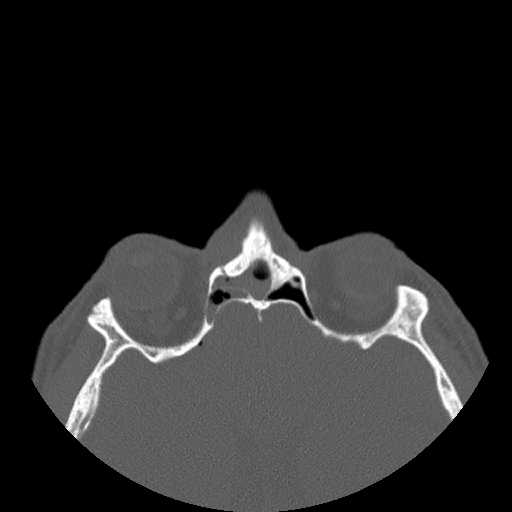
A more caudal axial image demonstrates the fracture line extending inferiorly through the right nasal bone resulting in minimal displacement.

Return to top
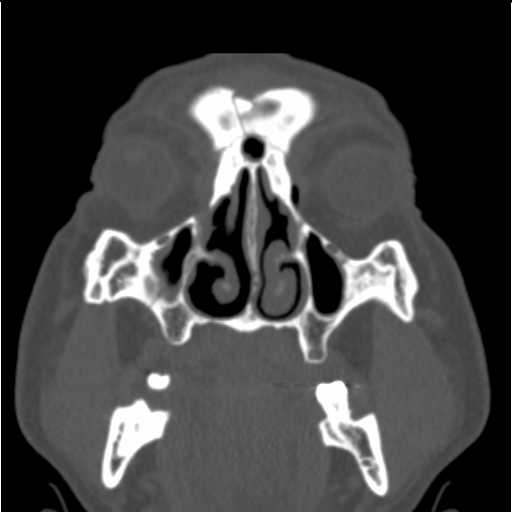
Coronal image demonstrates a complex fracture line through the outer table of the frontal bone at the level of the frontal sinus extending inferiorly to the nasal bones.

Return to top
A more posterior coronal image demonstrates a posteriorly displaced bony fragment in the midline of the frontal sinus.

Return to top

Return to top

Return to top

Return to top
Friends
 |
Orbital Rim |
 |
Lamina Papyrecea |
 |
Orbital Floor |
 |
Orbital Blowout |
Groups
 |
Orbital Fractures |
 |
Nasal Fractures |
 |
Tripod Fractures |
 |
LeFort Fractures |
 |
Smash Fractures |
 |
Mandibular Fractures |