
Mandibular Condyle
The condylar process of the mandible is defined as the portion of the mandible superior to the sigmoid notch and includes the mandibular portion of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). Condylar fractures are classified as extracapsular, subcondylar, or intracapsular. TMJ dislocation can occur from both directly blunt force and from pulling of the lateral pterygoid muscle on a fractured mandibular condyle. Condylar fractures that extend to the articular surface of the TMJ have can significant morbidity from resultant temporomandibular joint disorder.
Scrollable Stack Images
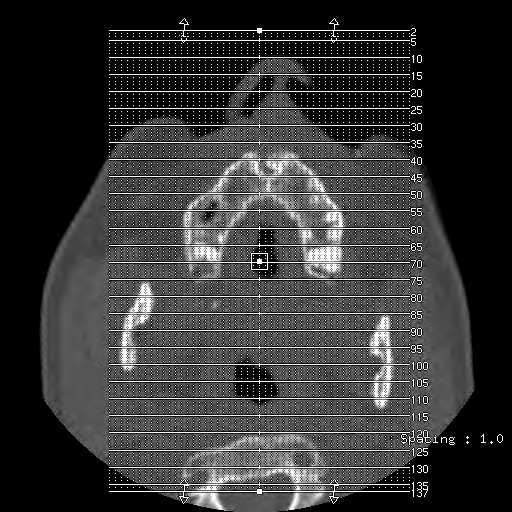
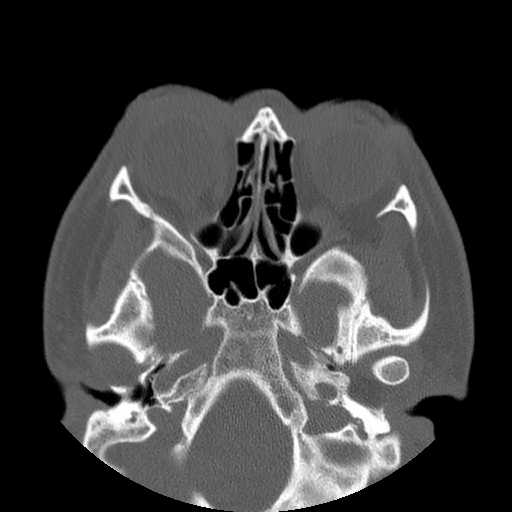
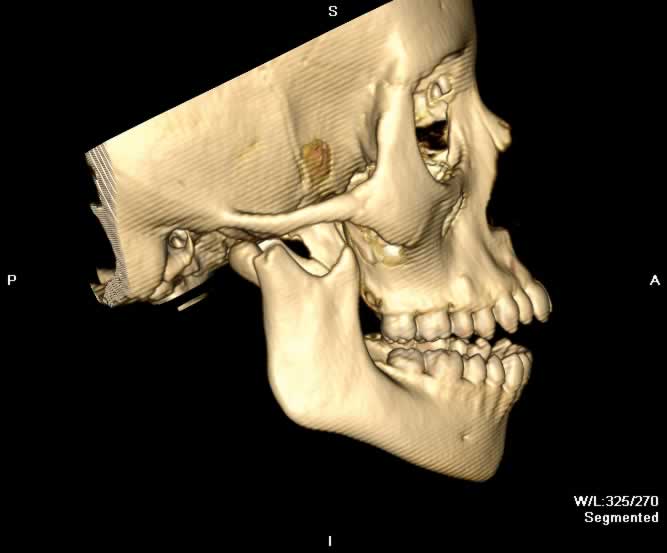
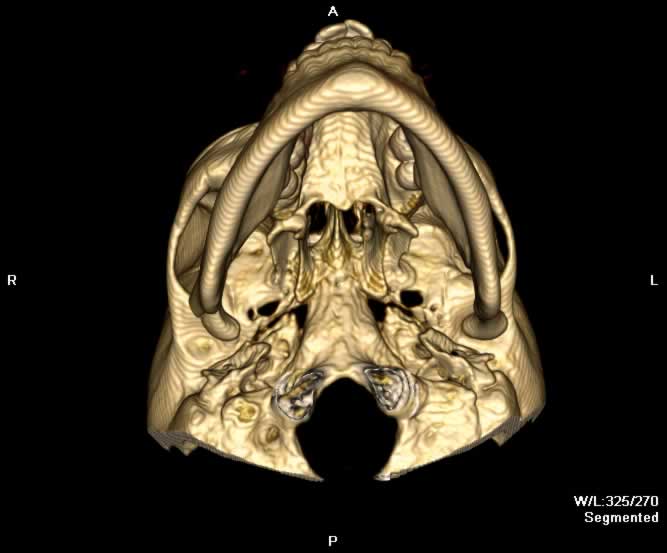
Images show a fracture of the mandibular condyle on the right. The fracture is transversely orientated at the level of the condylar neck. The fracture does not extend to the articular surface of the condylar head. Anteromedial displacement of the right mandibular condyle in relation to the temporomandibular joint can be appreciated. No additional mandibular fractures are seen.
Static 2D
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Click to enlarge | |||
Static 3D
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Click to enlarge | |||
Rotating 3D

Return to top
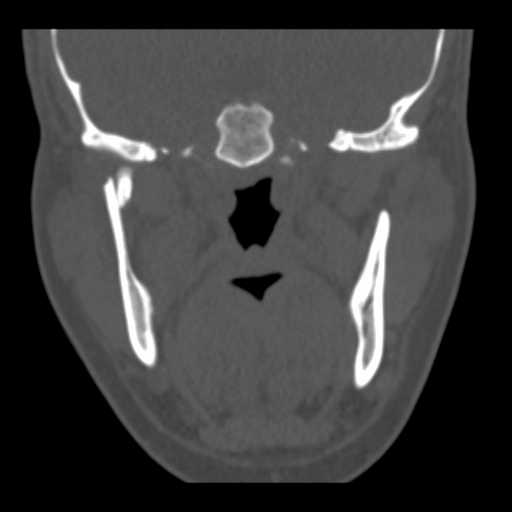
Coronal image demonstrates anteromedial displacement of the right mandibular condyle in relation to the temporomandibular joint.

Return to top
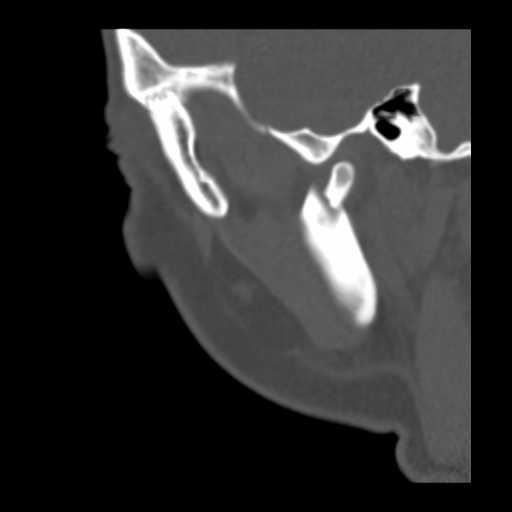
Coronal image demonstrates a displaced fracture traversing the mandibular condyle.

Return to top
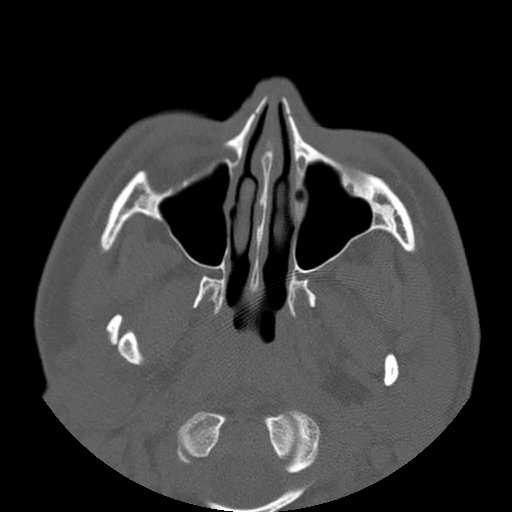
Axial image demonstrates anteromedial displacement of the right mandibular condyle.

Return to top
A more cephalad axial image demonstrates that the right temporomandibular joint fossa is empty.

Return to top

Return to top

Return to top

Return to top
Friends
 |
Mandibular Symphysis |
 |
Mandibular Body |
 |
Mandibular Angle |
Groups
 |
Orbital Fractures |
 |
Nasal Fractures |
 |
Tripod Fractures |
 |
LeFort Fractures |
 |
Smash Fractures |
 |
Mandibular Fractures |