
Moderate Tripod
Moderate and severe tripod fractures frequently extend to the infraorbital foramen and can result in infraorbital nerve injury. Moderate and severe tripod injuries are also seen in association with orbital floor or blowout fractures.
In severe tripod fractures, the zygoma fragment can be displaced posteriorly to the coronoid process, often preventing jaw closure. Severe tripod fractures may also have a fracture line extending posteriorly, disrupting the temporomandibular joint.
Scrollable Stack Images
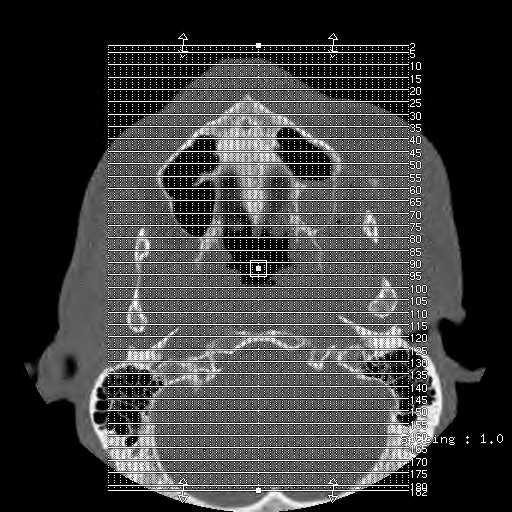
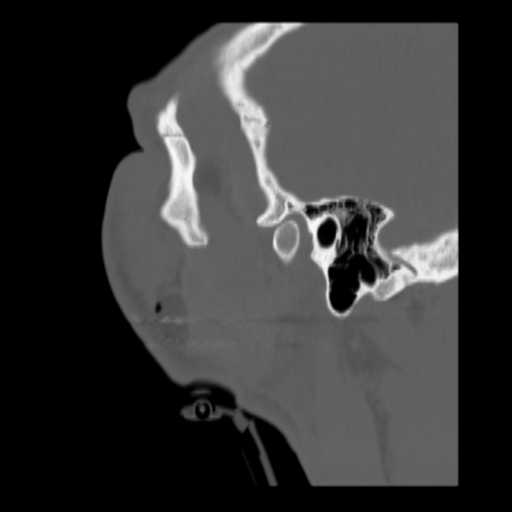
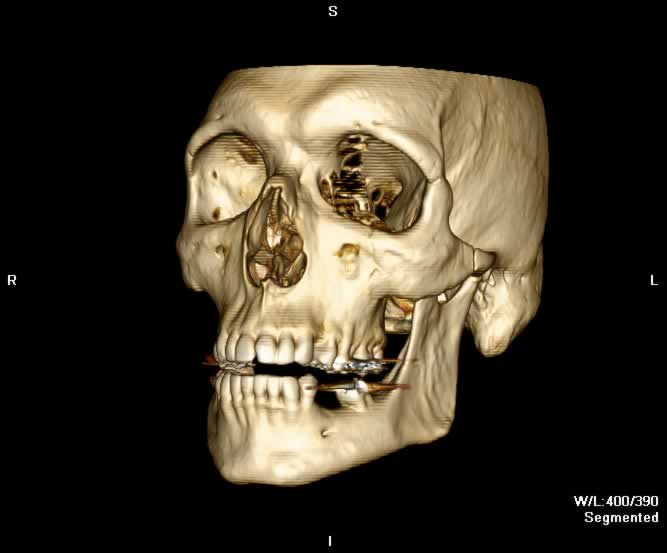
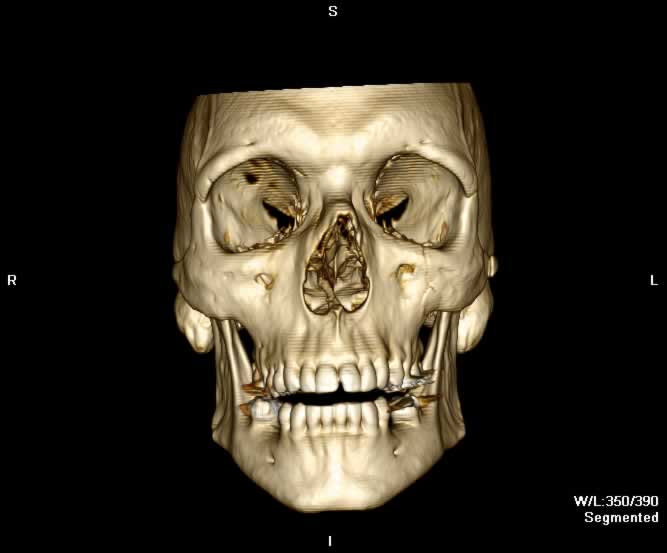
Images show a moderate tripod fracture on the left with slight depression of the zygomatic arch.
A displaced fracture through the left zygomaticotemporal suture is seen. Widening of the left frontozygomatic and zygomaticomaxillary sutures can be appreciated. Multiple fracture lines can be appreciated in the walls of the left maxillary sinus resulting in hemorrhage. Extensive soft tissue swelling overlying the left zygoma and maxilla is seen.
Static 2D
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Click to enlarge | |||
Static 3D
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Click to enlarge | |||
Rotating 3D

Return to top
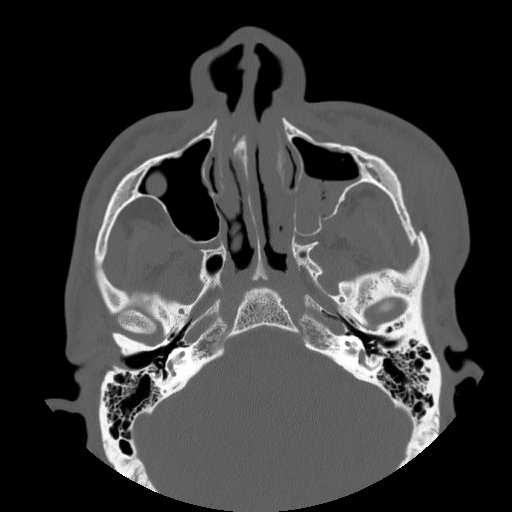
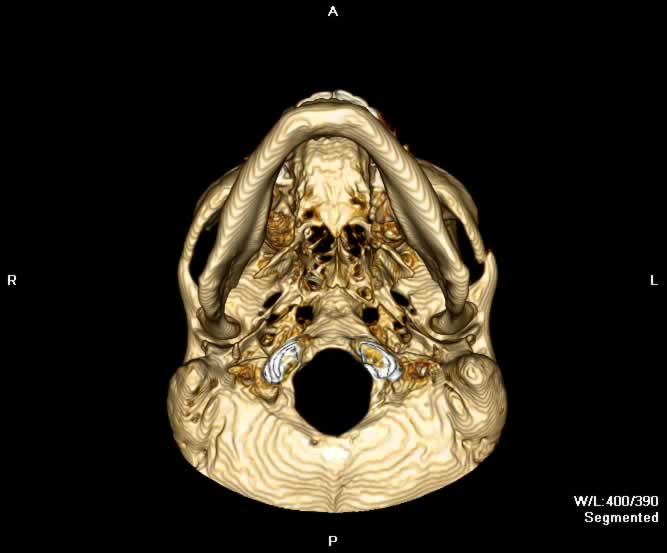
Axial image demonstrates a displaced fracture through the left zygomaticotemporal suture with depression of the zygoma. A fracture of the posterolateral wall of the left maxillary sinus is seen with hemorrhage.

Return to top
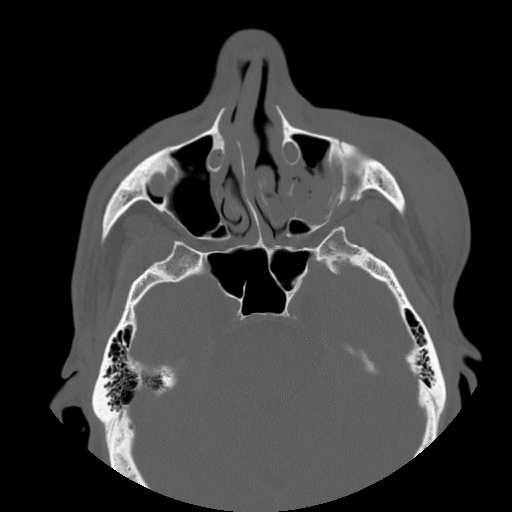
A more cephalad axial image demonstrates widening of the left zygomaticomaxillary suture.

Return to top
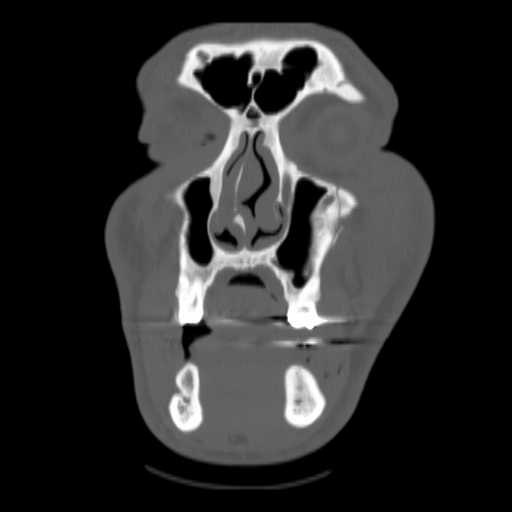
Coronal image demonstrates widening of the left frontozygomatic suture and a minimally displaced, vertically orientated fracture through the left zygomaticomaxillary suture.

Return to top
Sagittal image demonstrates minimal widening of the frontozygomatic suture.

Return to top

Return to top

Return to top

Return to top
Friends
 |
Mild Tripod |
 |
Severe Tripod |
Groups
 |
Orbital Fractures |
 |
Nasal Fractures |
 |
Tripod Fractures |
 |
LeFort Fractures |
 |
Smash Fractures |
 |
Mandibular Fractures |